- DR Rajshekhar KT
- 0 Comments
Avascular necrosis (AVN), also known as osteonecrosis, is a medical condition characterized by the death of bone tissue due to a lack of blood supply. This lack of blood supply can cause the affected bone to break down and ultimately collapse. AVN can occur in various bones throughout the body, but it most commonly affects the hip joint. In this comprehensive guide, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for avascular necrosis.
Causes of Avascular Necrosis:
Several factors can lead to avascular necrosis, including:
Trauma: A sudden injury or trauma to a bone, such as a fracture or dislocation, can damage blood vessels and disrupt blood flow to the bone.
Steroid Medications: Long-term or high-dose use of corticosteroid medications can impair blood circulation and increase the risk of AVN.
Alcohol Abuse: Excessive alcohol consumption can weaken bones and affect blood vessel health, making individuals more susceptible to AVN.
Joint Conditions: Certain joint conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus, can increase the risk of AVN.
Medical Conditions: Conditions like sickle cell disease, clotting disorders, and HIV can interfere with blood flow, contributing to AVN development.
Radiation Therapy: Cancer patients who receive radiation therapy near bones may develop AVN as a side effect.
Idiopathic: In some cases, the cause of AVN is unknown, referred to as idiopathic AVN.
Symptoms of Avascular Necrosis:
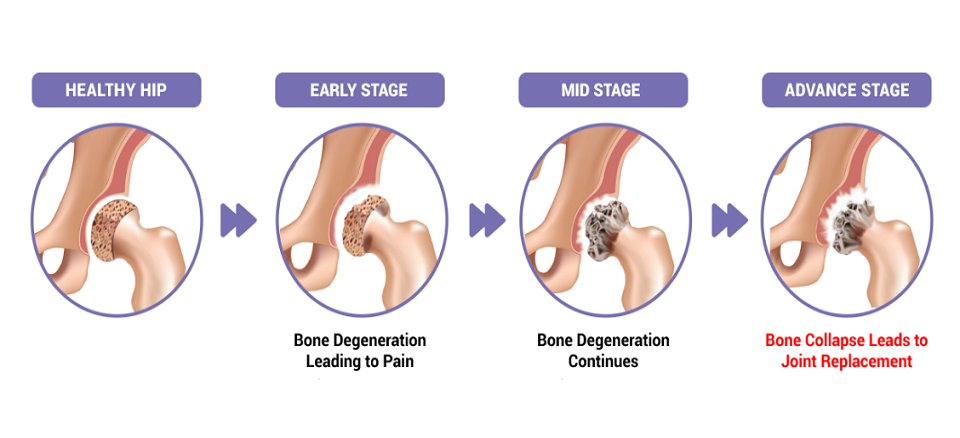
The symptoms of AVN can vary depending on the affected joint and the stage of the condition. Common symptoms include:
Joint Pain: Initially, patients may experience mild joint pain, which can progress to severe pain as the condition worsens.
Limited Range of Motion: As the joint deteriorates, it can become stiff, and patients may have difficulty moving it.
Joint Swelling: Swelling around the affected joint is common, especially during flare-ups.
Joint Instability: In advanced stages, the affected bone may collapse, causing instability and deformity in the joint.
Diagnosis of Avascular Necrosis:
Diagnosing AVN typically involves a combination of the following:
Medical History: Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, medical history, and any risk factors you may have.
Physical Examination: A physical exam can help assess joint function, range of motion, and any signs of joint instability.
Imaging: X-rays, MRI scans, and CT scans are commonly used to visualize bone damage and determine the extent of AVN.
Blood Tests: These tests can help identify underlying conditions that may contribute to AVN, such as clotting disorders.
Treatment Options for Avascular Necrosis:
The treatment of AVN depends on several factors, including the stage of the disease, the affected joint, and the underlying cause. Treatment options include:
Medications: Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications can help manage pain and inflammation associated with AVN.
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy exercises can improve joint strength and flexibility, reducing pain and enhancing mobility.
Assistive Devices: The use of crutches, braces, or other assistive devices may be recommended to reduce stress on the affected joint.
Core Decompression: This surgical procedure involves removing a portion of the damaged bone and drilling holes to stimulate the growth of new blood vessels and bone tissue.
Bone Grafting: In more advanced cases, a bone graft may be necessary to replace the damaged bone with healthy bone tissue.
Joint Replacement: Total joint replacement surgery may be recommended when the joint is severely damaged and non-surgical options are ineffective.
Biological Therapies: Emerging treatments, such as stem cell therapy or growth factor injections, are being explored to promote bone healing in AVN.
Lifestyle Changes: Patients are often advised to make lifestyle changes, such as reducing alcohol consumption and discontinuing the use of steroids, to prevent further damage.
It’s important to note that early detection and intervention are crucial for the successful treatment of avascular necrosis. If you suspect you have symptoms of AVN or are at risk, consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan.